hello boys&girls, i made my probes(just cutted the minijack cable from an old microphone and solder them to solidcore wire), and im using the software "Soundcard Oszilloscope", because it is freeware...
but when i was going to try this thing, the software dont show me any data... how do i know whats the negative/positive on my probes? i also tryed reversing the clips but nothing... if anyone can help it will be great!
Difficulty: Moderately Challenging
Instructions
Things You'll Need:
Sound card
PC
Sound card oscilloscope software
Old headphone cable (1/8 in. jack)
Soldering iron
Solid core wire
DC Power Supply
Voltmeter
Resistors or Potentiometer
Step 1
Download PC sound card oscilloscope software. Some of the more commonly used software includes Zelscope, Audiotester and Scope, which can all be downloaded at little or no charge to the user (see Resources below).
Step 2
Configure your PC to record sound via the microphone or line in port. Though you may not actually be recording any of the signals you'll be capturing, the PC sound card oscilloscope software uses the same interface used to record sound. Double-click on the volume icon in the system tray and be sure both the Line Volume and Microphone Volume levels are turned up and not muted.
Step 3
Make a set of probes. This requires an old headphone cable with an 1/8 inch phono jack, a soldering iron and some solid core wire. Cut off a long section of the wire and strip the ends opposite of the phono jack. There should be three wires if the phono jack is stereo, only two if the phono jack is mono.
Step 4
Solder solid core wire to the ends of each wire. Solid core wire can be plugged directly into breadboards or used as probes. If you desire, you could solder banana clips, alligator clips or any type of connector or probe to the ends of the wires.
Step 5
Make a voltage divider. A voltage divider is required because your sound card was intended to be used with low-power audio devices. The maximum voltage from your circuit should be around 1.7v. The sound card should be protected against some voltage spikes, but anything above 5v may permanently damage your sound card. A voltage divider can be created with resistors or a potentiometer.
Step 6
Test the voltage divider. Since the voltage divider may be the only thing protecting your sound card from the higher-voltage circuit, supply a DC voltage of the maximum voltage your circuit can output. Measure the output of the voltage divider. Remember, you're aiming for an output voltage peaking at 1.7v or lower.
Step 7
Start the PC oscilloscope software. Once started, you will see an oscilloscope-like interface. You may also want to turn down the volume of your speakers as many waveforms can sound very loud or even damage your speakers.
Step 8
Test your circuit with the probes. Though you won't be able to probe the circuit as freely as you would with a real oscilloscope, you will at least be able to get some information about what's happening in your circuit.
Read more: How to Use Your Sound Card as an Oscilloscope | eHow.com How to Use Your Sound Card as an Oscilloscope | eHow.com
but when i was going to try this thing, the software dont show me any data... how do i know whats the negative/positive on my probes? i also tryed reversing the clips but nothing... if anyone can help it will be great!
Difficulty: Moderately Challenging
Instructions
Things You'll Need:
Sound card
PC
Sound card oscilloscope software
Old headphone cable (1/8 in. jack)
Soldering iron
Solid core wire
DC Power Supply
Voltmeter
Resistors or Potentiometer
Step 1
Download PC sound card oscilloscope software. Some of the more commonly used software includes Zelscope, Audiotester and Scope, which can all be downloaded at little or no charge to the user (see Resources below).
Step 2
Configure your PC to record sound via the microphone or line in port. Though you may not actually be recording any of the signals you'll be capturing, the PC sound card oscilloscope software uses the same interface used to record sound. Double-click on the volume icon in the system tray and be sure both the Line Volume and Microphone Volume levels are turned up and not muted.
Step 3
Make a set of probes. This requires an old headphone cable with an 1/8 inch phono jack, a soldering iron and some solid core wire. Cut off a long section of the wire and strip the ends opposite of the phono jack. There should be three wires if the phono jack is stereo, only two if the phono jack is mono.
Step 4
Solder solid core wire to the ends of each wire. Solid core wire can be plugged directly into breadboards or used as probes. If you desire, you could solder banana clips, alligator clips or any type of connector or probe to the ends of the wires.
Step 5
Make a voltage divider. A voltage divider is required because your sound card was intended to be used with low-power audio devices. The maximum voltage from your circuit should be around 1.7v. The sound card should be protected against some voltage spikes, but anything above 5v may permanently damage your sound card. A voltage divider can be created with resistors or a potentiometer.
Step 6
Test the voltage divider. Since the voltage divider may be the only thing protecting your sound card from the higher-voltage circuit, supply a DC voltage of the maximum voltage your circuit can output. Measure the output of the voltage divider. Remember, you're aiming for an output voltage peaking at 1.7v or lower.
Step 7
Start the PC oscilloscope software. Once started, you will see an oscilloscope-like interface. You may also want to turn down the volume of your speakers as many waveforms can sound very loud or even damage your speakers.
Step 8
Test your circuit with the probes. Though you won't be able to probe the circuit as freely as you would with a real oscilloscope, you will at least be able to get some information about what's happening in your circuit.
Read more: How to Use Your Sound Card as an Oscilloscope | eHow.com How to Use Your Sound Card as an Oscilloscope | eHow.com


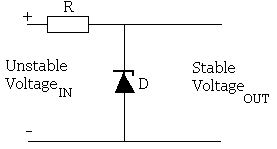


 im so happy!
im so happy!







Comment