The Four Quadrant Theory of Electrical Activity, Part Two, or more? (1 of 7)
In part one the energy transfer was one only of two forms, the transfer of Magnetic Energy, or the transfer of Dielectric Energy. Only one form of Inductive Energy exists. It is a single energy, and accordingly it is called a Single Energy Transient. Only one form of stored energy is active in a Single Energy Transient.
This stored energy can exist in one of two distinct forms,
The Magnetic Energy,
(1)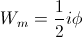 , Ampere-Weber
, Ampere-Weber
The Dielectric Energy,
(2)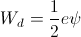 , Volt-Coulomb
, Volt-Coulomb
Because these stored energies are static quantities, they are time invariant. The dimension of time has no role in their existence. It is however that time is a necessary dimensional requirement for the existence of energy. So where then is the energy?
These dimensional expressions for stored energy represent only the Potential for Energy Existence. It is that the expressions given for the energy stored by a field of induction are no more than expressions for the magnitude, and quantity, of the magnetic induction, and dielectric induction, themselves. No union of the two inductions exist to form the product, Electrification, Q, and its time rate, Energy, W.
The single energy transient is a Magnetic Energy Transient, a transient of Electro-Motive Force, E, or it is a Dielectric Energy Transient, a transient of Displacement Current, I. These two reactive transients give rise to products, these with their respective potentials, the electro-static potential, e, and the magneto-motive force, i. M.M.F. is also considered a potential in that it is static. These products of reaction and potential represent The Electrical Activity of their respective Single Energy Transients. Thus a pair of Products, one for each field,
The Magnetic Activity
(3)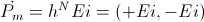 , Watt
, Watt
The Dielectric Activity
(4)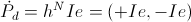 , Watt.
, Watt.
Each Versor Activity,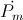 or
or 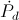 , represents one form of energy only, magnetic or dielectric, not both.
, represents one form of energy only, magnetic or dielectric, not both.
Also shown in part one was the magnification factor is a negative numeric. This magnification factor, n, is the ratio of two time spans, the time span for charge, to the time span for discharge. For the numeric ratio to be negative, one time span must also be negative. Hence the magnification factor is the ratio of a negative time span, the charge time, to a positive time span, the discharge time. The magnification factor is given as
(5)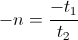 , Numeric
, Numeric
By the Law of Energy Conservation for the stored inductive energy, the amount of energy given to the field must equal the amount of energy that the field can give back. This is to say the energy sent into a field of induction is the same energy sent out of the field of induction. Hence the two energies are in opposition with regard to the flow of power, the power in, and the power out, this resulting in a negative transfer constant, the magnification factor, n.
This results in the expressions for power flow containing a negative dimension, now exists one power flow forward in time, and another power flow, reverse in time. Power can now flow in both directions with regard to the dimension of time. Hence Power is free to move about in the dimension of Time, that is, it is a Versor Power Flow.
Here exists an analog of power flow in space along the length of a transmission line, where power is free to move along the length of the line in either direction. Thus the analog of a “Length of Time”. Here then the existence of forward and reflected waves in time, just as was seen for waves on a transmission line. Hereby a composite transient, the superposition of a wave moving forward in time and a wave moving backward in time, can be developed for any instant in time. One wave travels from the past to the future, the other wave travels from the future to the past, a pair of traveling waves in time, traveling in opposite directions. The superposition of the opposing waves is the Present, or Now, t equals zero.
The versor of Electrical Activity hence resides in the metrical dimension of Time, giving the relation as
(6)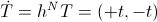 , Seconds.
, Seconds.
Time is now a bi-valent dimension, two values of time,
+ t , real time, seconds,
- t , imaginary time, seconds.
It is then given by the Law of Energy Conservation,
(7)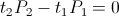 , Watt-Second
, Watt-Second
Imaginary Time can be called “Counter – Time”, this in analog to “Counter – Space”. There is however an important difference between the two. The expression for Counter-Space is given by
(8)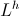 , Per Centimeter
, Per Centimeter
Where h = -1
However, the expression for Counter-Time is given by
(9)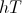 , Negative Second
, Negative Second
Space is given here in terms of algebraic products, whereas Time is given here in terms of algebraic sums. This suggests a relation between Time and Space, or Time – Space where it is
(10)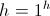 , Versor
, Versor
(10a)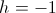 , Unit Versor
, Unit Versor
A similar condition can be found for the versor condition
(11)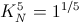 , Versor
, Versor
Reducing this to a base two versor,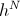 , gives the pair of projections,
, gives the pair of projections,
In part one the energy transfer was one only of two forms, the transfer of Magnetic Energy, or the transfer of Dielectric Energy. Only one form of Inductive Energy exists. It is a single energy, and accordingly it is called a Single Energy Transient. Only one form of stored energy is active in a Single Energy Transient.
This stored energy can exist in one of two distinct forms,
The Magnetic Energy,
(1)
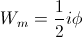 , Ampere-Weber
, Ampere-WeberThe Dielectric Energy,
(2)
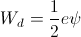 , Volt-Coulomb
, Volt-CoulombBecause these stored energies are static quantities, they are time invariant. The dimension of time has no role in their existence. It is however that time is a necessary dimensional requirement for the existence of energy. So where then is the energy?
These dimensional expressions for stored energy represent only the Potential for Energy Existence. It is that the expressions given for the energy stored by a field of induction are no more than expressions for the magnitude, and quantity, of the magnetic induction, and dielectric induction, themselves. No union of the two inductions exist to form the product, Electrification, Q, and its time rate, Energy, W.
The single energy transient is a Magnetic Energy Transient, a transient of Electro-Motive Force, E, or it is a Dielectric Energy Transient, a transient of Displacement Current, I. These two reactive transients give rise to products, these with their respective potentials, the electro-static potential, e, and the magneto-motive force, i. M.M.F. is also considered a potential in that it is static. These products of reaction and potential represent The Electrical Activity of their respective Single Energy Transients. Thus a pair of Products, one for each field,
The Magnetic Activity
(3)
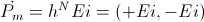 , Watt
, WattThe Dielectric Activity
(4)
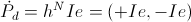 , Watt.
, Watt.Each Versor Activity,
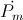 or
or 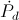 , represents one form of energy only, magnetic or dielectric, not both.
, represents one form of energy only, magnetic or dielectric, not both.Also shown in part one was the magnification factor is a negative numeric. This magnification factor, n, is the ratio of two time spans, the time span for charge, to the time span for discharge. For the numeric ratio to be negative, one time span must also be negative. Hence the magnification factor is the ratio of a negative time span, the charge time, to a positive time span, the discharge time. The magnification factor is given as
(5)
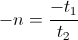 , Numeric
, NumericBy the Law of Energy Conservation for the stored inductive energy, the amount of energy given to the field must equal the amount of energy that the field can give back. This is to say the energy sent into a field of induction is the same energy sent out of the field of induction. Hence the two energies are in opposition with regard to the flow of power, the power in, and the power out, this resulting in a negative transfer constant, the magnification factor, n.
This results in the expressions for power flow containing a negative dimension, now exists one power flow forward in time, and another power flow, reverse in time. Power can now flow in both directions with regard to the dimension of time. Hence Power is free to move about in the dimension of Time, that is, it is a Versor Power Flow.
Here exists an analog of power flow in space along the length of a transmission line, where power is free to move along the length of the line in either direction. Thus the analog of a “Length of Time”. Here then the existence of forward and reflected waves in time, just as was seen for waves on a transmission line. Hereby a composite transient, the superposition of a wave moving forward in time and a wave moving backward in time, can be developed for any instant in time. One wave travels from the past to the future, the other wave travels from the future to the past, a pair of traveling waves in time, traveling in opposite directions. The superposition of the opposing waves is the Present, or Now, t equals zero.
The versor of Electrical Activity hence resides in the metrical dimension of Time, giving the relation as
(6)
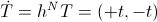 , Seconds.
, Seconds.Time is now a bi-valent dimension, two values of time,
+ t , real time, seconds,
- t , imaginary time, seconds.
It is then given by the Law of Energy Conservation,
(7)
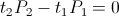 , Watt-Second
, Watt-SecondImaginary Time can be called “Counter – Time”, this in analog to “Counter – Space”. There is however an important difference between the two. The expression for Counter-Space is given by
(8)
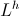 , Per Centimeter
, Per CentimeterWhere h = -1
However, the expression for Counter-Time is given by
(9)
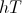 , Negative Second
, Negative SecondSpace is given here in terms of algebraic products, whereas Time is given here in terms of algebraic sums. This suggests a relation between Time and Space, or Time – Space where it is
(10)
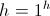 , Versor
, Versor(10a)
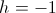 , Unit Versor
, Unit VersorA similar condition can be found for the versor condition
(11)
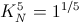 , Versor
, VersorReducing this to a base two versor,
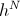 , gives the pair of projections,
, gives the pair of projections,
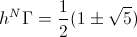 , Numeric
, Numeric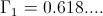 , Numeric
, Numeric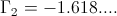 , Numeric.
, Numeric.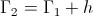 , Numeric
, Numeric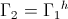 , Numeric
, Numeric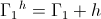 , Numeric
, Numeric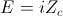 , Volts
, Volts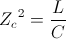 , Henry Per Farad
, Henry Per Farad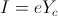 , Ampere
, Ampere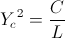 , Farad per Henry
, Farad per Henry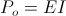 , Volt-Ampere
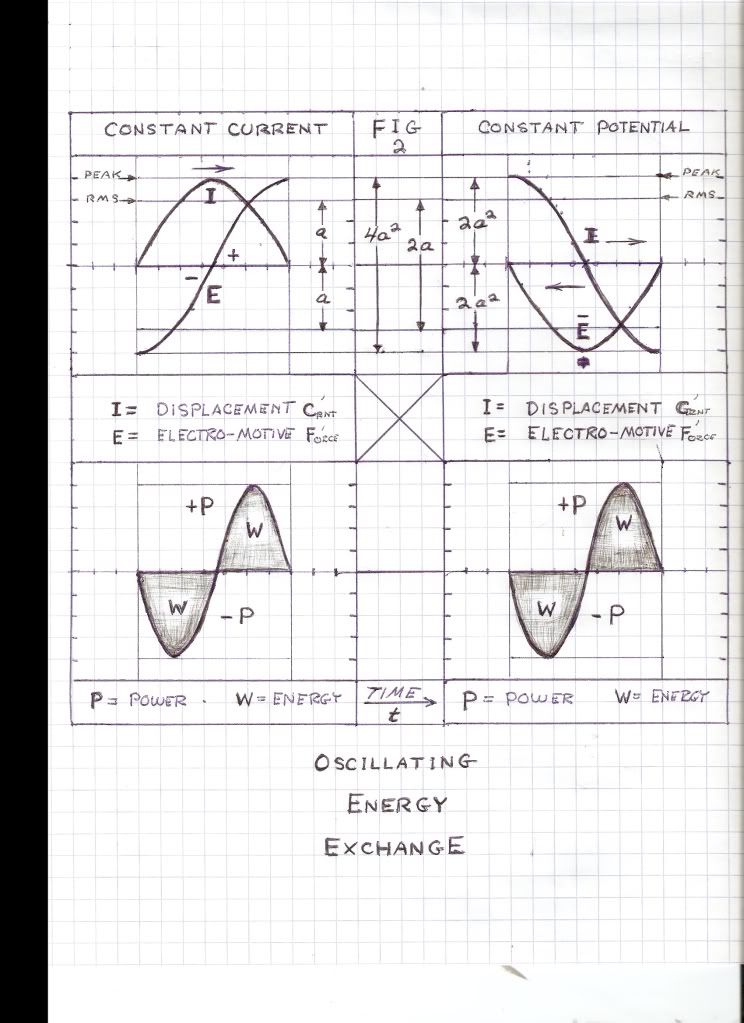
, Volt-Ampere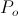 , in volt-amperes. This activity represents the flow of power between the Inductor and the Condenser. Rather than a single energy transfer, it is now a pair of energy transfers. This is now a double energy transfer, or a Double Energy Transient.
, in volt-amperes. This activity represents the flow of power between the Inductor and the Condenser. Rather than a single energy transfer, it is now a pair of energy transfers. This is now a double energy transfer, or a Double Energy Transient.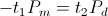 , watt-second
, watt-second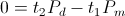 , watt-second
, watt-second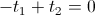 , seconds
, seconds
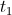 , and the discharge time span,
, and the discharge time span, 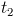 , are now equal and opposite. Hence a single time span can represent both
, are now equal and opposite. Hence a single time span can represent both 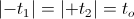 , seconds.
, seconds.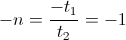 , versor.
, versor.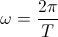 , radian per second
, radian per second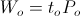 watt-second
watt-second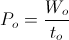 watt, or volt-ampere.
watt, or volt-ampere.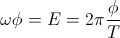 , weber per second
, weber per second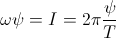 , coulomb per second
, coulomb per second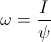 , and
, and 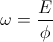 , radians per second
, radians per second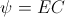 , and
, and 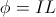 , Induction
, Induction
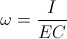 , and
, and 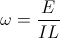 , radians per second
, radians per second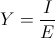 , and
, and 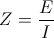 siemens, ohm
siemens, ohm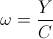 , and
, and 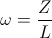 , radians per second
, radians per second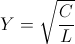 , and
, and 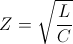 , siemens – ohm
, siemens – ohm 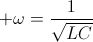 , and
, and 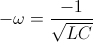 , radian per second
, radian per second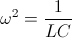 , by definition.
, by definition.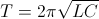 , seconds
, seconds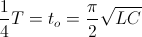 , seconds
, seconds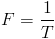 , per second
, per second
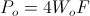 , volt – amperes
, volt – amperes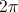 radian) per second. Hence the magnification of activity for a given quantity of energy in the oscillating energy exchange is not a function of the ratio of charge to discharge times, since they are now equal. The magnification is here given as a function of the rate of energy exchange, the Frequency of Oscillation, F, in cycles per second. The more rapid the energy exchange, the higher the frequency and thus the larger the magnitude of the resulting electric activity. Power is directly proportional to frequency.
radian) per second. Hence the magnification of activity for a given quantity of energy in the oscillating energy exchange is not a function of the ratio of charge to discharge times, since they are now equal. The magnification is here given as a function of the rate of energy exchange, the Frequency of Oscillation, F, in cycles per second. The more rapid the energy exchange, the higher the frequency and thus the larger the magnitude of the resulting electric activity. Power is directly proportional to frequency.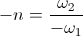 , numeric
, numeric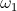 is the angular time rate of charge and
is the angular time rate of charge and 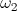 is the angular time rate of discharge. This magnification was utilized by Nikola Tesla for the purpose of Power Amplification with no electronic elements.
is the angular time rate of discharge. This magnification was utilized by Nikola Tesla for the purpose of Power Amplification with no electronic elements.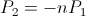 , volt-ampere
, volt-ampere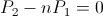 , volt-ampere
, volt-ampere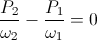 , volt-ampere-second
, volt-ampere-second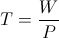 , joule per watt
, joule per watt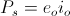 , watt
, watt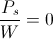 , per second
, per second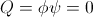 , planck.
, planck.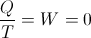 , joule
, joule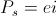 , watt.
, watt.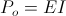 , volt-ampere
, volt-ampere
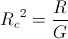 , ohm per siemens
, ohm per siemens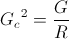 , siemens per ohm
, siemens per ohm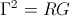 , scalar numeric.
, scalar numeric.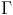 , the propagation constant.
, the propagation constant.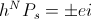 , watts
, watts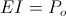 , volt-amperes,
, volt-amperes,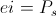 , watts.
, watts.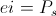 , watt
, watt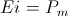 , joule per second
, joule per second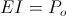 , volt-ampere
, volt-ampere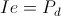 , joule per second
, joule per second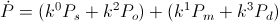
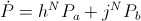 , versor watt
, versor watt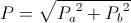 , watt
, watt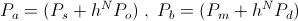 , watt
, watt
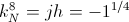 , versor
, versor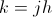 , versor
, versor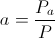 , Power Factor, percent
, Power Factor, percent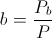 , Induction Factor, percent
, Induction Factor, percent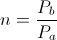 , Magnification Factor, numeric
, Magnification Factor, numeric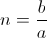 , numeric
, numeric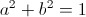 , unity
, unity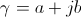 , versor
, versor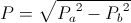 , watt
, watt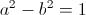 , unity
, unity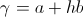 , versor
, versor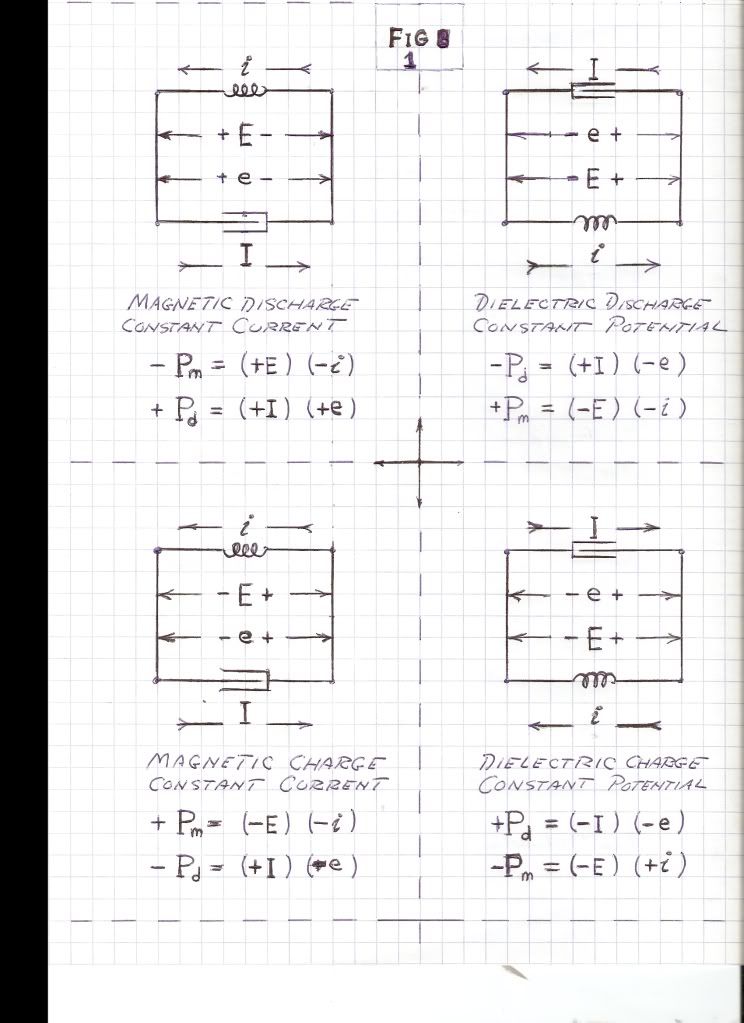
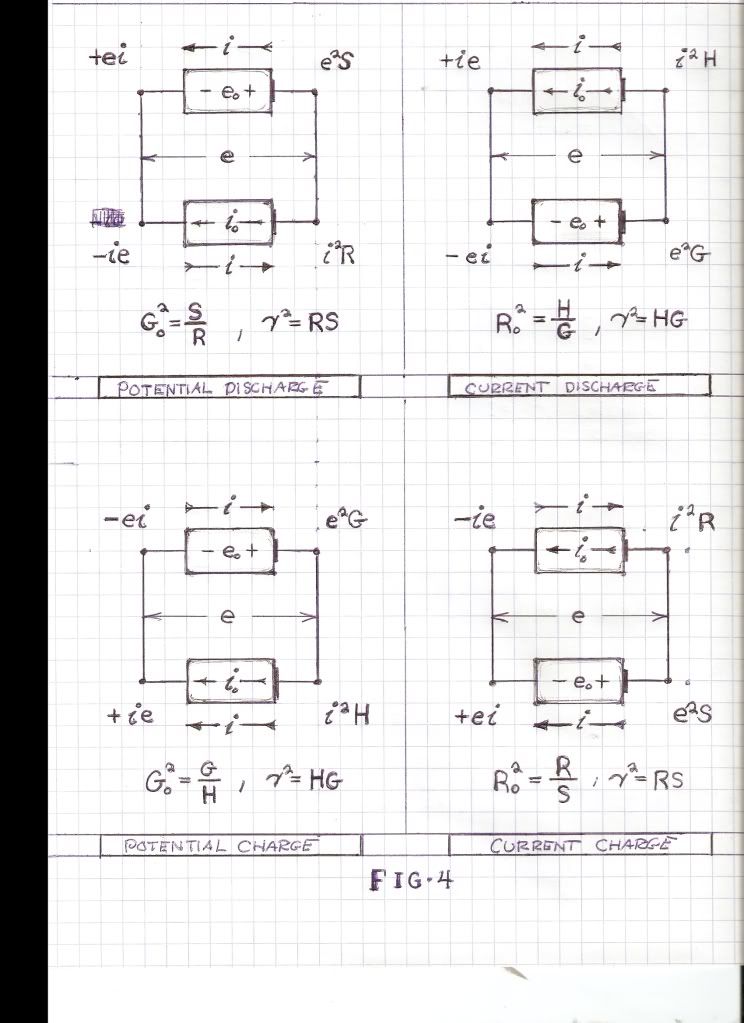
Comment